Laser system
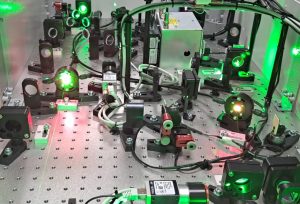
Photocathode laser, amplifier stages
The SPARC_LAB photocathode laser system is based on a Titanium-Sapphire laser at about 800 nm and its harmonics. The laser system is synchronized with the RF system and based on the Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) of the pulse (the same scheme awarded by the 2018 Nobel prize) with a layout similar to the FLAME laser. In 2023 we refurbished the system with a new laser (CPA from Amplitude, oscillator from Coherent) in the framework of Sabina project to have a compressed energy of about 100 mJ and pulses below 50 fs FWHM. We split the IR laser pulses into two branch: one for the photocathode and one for FEL seeding and diagnostics. The photocathode pulses are then up-converted via harmonic generation to the 3rd harmonic at 263 nm, the wavelength required for electron extraction. We developed a system capable of generating a longitudinal train of pulses used for the Comb Beam, needed in two color FEL or plasma acceleration experiments. We use the imaging of an iris to obtain a quasi-flat-top laser profile on the cathode (like the image below). A transport line delivers the other IR laser pulse from the laser room to the FEL and diagnostic (in particular to the Electro-Optic Sampling) along the electron beamline. More recently, we started using the second harmonic at 389 nm on the cathode, using two photon absorption for the electron generation for configurations of very short pulses (<200 fs).
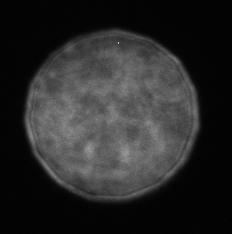
UV profile on the cathode

Laser clean room at the end of the commissioning of the new system
| Laser system parameters | reference (capability) |
|---|---|
| Laser oscillator central wavelength (nm) | 775 (750-850) |
| Laser oscillator bandwidth (nm) | 45 (30-100) |
| Laser oscillator rep rate (MHz) | 79.333 |
| Laser min IR FWHM pulse length @ compressor exit (fs) | 40 |
| Laser UV FWHM pulse length capability @ cathode (ps) | <0.1 – 10 |
| Max laser pulse energy in IR (mJ) | 100 |
| Max laser pulse energy in UV (mJ) | 1 |
| Repetition rate (Hz) | 10 |
| Rms energy jitter in UV (shot-to-shot) (%) | 2 (1-3) |
| Rms pointing stability on cathode (µm) | 15 |
RF gun

SPARC_LAB RF gun
The photocathode is composed by a 1.6 cell RF gun operated at S-band (2.856 GHz, of BNL/UCLA/SLAC type) with a high peak field on the cathode (120 MV/m) generating 5 MeV electron beam. It has two laser access points: one at 70° of incidence from viewports beside the photocathode and one at 3° of incidence with an off-axis mirror just outside the vacuum chamber at about 0.5 m from the cathode. Quantum efficiency is typically in the order of $10^{-5}$ for our copper cathode and we measured intrinsic emittance of 0.7 mm mrad /mm. A four-coil solenoid assembly approximately 20 cm in length is inserted after the RF gun. This element is crucial for emittance minimization to have high brightness electron beam, in a configuration where a double minimum in emittance is generated along the line. After the solenoid there is a small diagnostic station for beam characterization in transverse dimension, energy, charge and emittance.
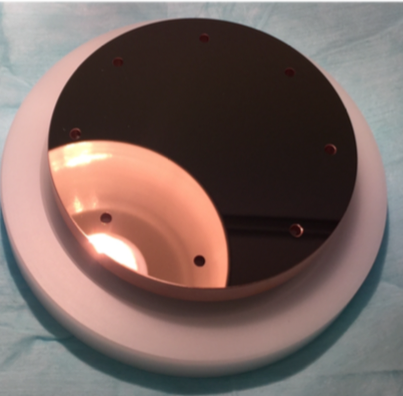
Surface of the polycrystalline oxigen-free copper cathode
| Photocathode system parameters | |
|---|---|
| Maximum peak field on the cathode | 120 MV/m |
| Repetition rate | 10 Hz |
| Operating vacuum | $10^{-9}$ Torr |
| Quantum efficiency max (typical) | $10^{-5} (5 \cdot 10^{-6})$ |
| Maximum gun solenoid field | 0.3 T |
| Laser central wavelength | 263 nm |
| RF frequency | 2.856 GHz |
| RMS intrinsic emittance | 0.7 mm mrad/mm |
| Beam charge | 10-1000 pC |
| Number of cells | 1.6 |
Publication highlights:
- “RF and Magnetic Measurements on the SPARC Photoinjector and Solenoid at UCLA”, J.B. Rosenzweig et al., PAC conference 2005 doi: 10.1109/PAC.2005.1591206
- “Laser comb with velocity bunching: Preliminary results at SPARC”, M. Ferrario et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A vol. 637 (2011) pag. S43, doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2010.02.018
- “Laser pulse shaping for multi-bunches photoinjectors”, F. Villa et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A vol. 740 (2014) pag. 188, doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2013.11.060
- “Laser pulse shaping for high gradient accelerators”, F. Villa et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A vol. 829 (2016) pag. 446, doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2016.01.010
- “Nano-machining, surface analysis and emittance measurements of a copper photocathode at SPARC_LAB”, J. Scifo et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A vol. 909 (2018) pag. 233, doi:10.1016/j.nima.2018.01.041
- “Time-resolved study of nonlinear photoemission in radio-frequency photoinjectors”, R. Pompili et al., Opt. Lett. vol. 46 (2021) pag. 2844, doi: 10.1364/OL.423880
- “Design and realization of new solenoids for high brightness electron beam injectors”, A. Vannozzi et al., Proceedings of 12th IPAC (2021), pag. TUPAB366, doi: 10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2021-TUPAB366
- “The new C band gun for the next generation RF photo-injectors”, D. Alesini et al., Proceedings of 13th IPAC (2022), pag. MOPOMS021, doi: 10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2022-MOPOMS021
- “Dark current studies for a high gradient SW C-band RF gun”, F. Cardelli et al., Proceedings of 13th IPAC (2022), pag. MOPOMS020, doi: 10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2022-MOPOMS020
Contact person:
F. Villa, fabio.vila@lnf.infn.it, tel. (+39) 069403 2347

